Pinecone Integration
Pricing
Pay per usage
Pinecone Integration
This integration transfers data from Apify Actors to a Pinecone and is a good starting point for a question-answering, search, or RAG use case.
4.6 (5)
Pricing
Pay per usage
30
Monthly users
91
Runs succeeded
>99%
Response time
4 days
Last modified
a day ago
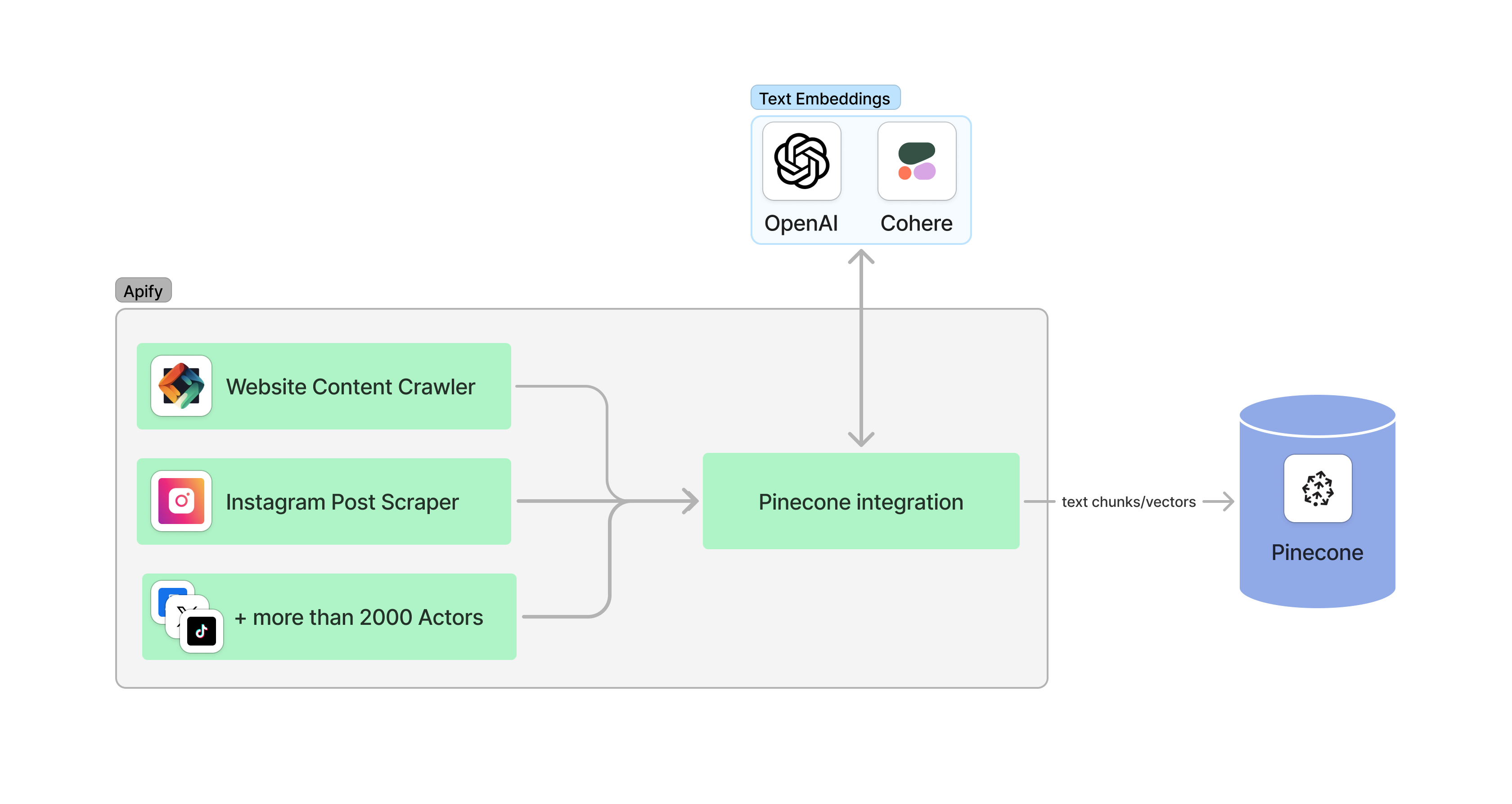
The Apify Pinecone integration transfers selected data from Apify Actors to a Pinecone database. It processes the data, optionally splits it into chunks, computes embeddings, and saves them to Pinecone.
This integration supports incremental updates, updating only the data that has changed. This approach reduces unnecessary embedding computation and storage operations, making it suitable for search and retrieval augmented generation (RAG) use cases.
💡 Note: This Actor is meant to be used together with other Actors' integration sections. For instance, if you are using the Website Content Crawler, you can activate Pinecone integration to save web data as vectors to Pinecone.
For more information how to leverage vector stores in Apify platform, see detailed blog post What Pinecone is and why you should use it with your LLMs. For setup instructions in the Apify Console, see the Pinecone integration guide.
What is Pinecone vector database?
Pinecone is a cloud-native vector database designed to manage high-dimensional vector data efficiently. Its core functionality is based on the Approximate Nearest Neighbor (ANN) search, which quickly identifies and ranks matches within large datasets. The serverless architecture of Pinecone enables rapid development and deployment of powerful applications. Pinecone supports clients in Python, Java, Node.js, and Golang.
📋 How does the Apify-Pinecone integration work?
Apify Pinecone integration computes text embeddings and store them in Pinecone. It uses LangChain to compute embeddings and interact with Pinecone.
- Retrieve a dataset as output from an Actor
- [Optional] Split text data into chunks using
langchain'sRecursiveCharacterTextSplitter(enable/disable usingperformChunkingand specifychunkSize,chunkOverlap) - [Optional] Update only changed data (select
dataUpdatesStrategy) - Compute embeddings, e.g. using
OpenAIorCohere(specifyembeddingsProviderandembeddingsConfig) - Save data into the database
✅ Before you start
To utilize this integration, ensure you have:
- Created or existing
Pineconedatabase. You need to knowindexNameandapiKey. - An account to compute embeddings using one of the providers, e.g., OpenAI or Cohere.
👉 Examples
The configuration consists of three parts: Pinecone, embeddings provider, and data.
Ensure that the vector size of your embeddings aligns with the configuration of your Pinecone index.
For instance, if you're using the text-embedding-3-small model from OpenAI, it generates vectors of size 1536.
This means your Pinecone index should also be configured to accommodate vectors of the same size, 1536 in this case.
For detailed input information refer to the Input page.
Database: Pinecone
1{ 2 "pineconeApiKey": "YOUR-PINECONE-API-KEY", 3 "pineconeIndexName": "apify" 4}
Embeddings provider: OpenAI
1{ 2 "embeddingsProvider": "OpenAI", 3 "embeddingsApiKey": "YOUR-OPENAI-API-KEY", 4 "embeddingsConfig": {"model": "text-embedding-3-large"} 5}
Embeddings provider: Cohere
1{ 2 "embeddingsApiKey": "YOUR-COHERE-API-KEY", 3 "embeddingsProvider": "Cohere", 4 "embeddingsConfig": {"model": "embed-multilingual-v3.0"} 5}
Save data from Website Content Crawler to Pinecone
Data is transferred in the form of a dataset from Website Content Crawler, which provides a dataset with the following output fields (truncated for brevity):
1{ 2 "url": "https://www.apify.com", 3 "text": "Apify is a platform that enables developers to build, run, and share automation tasks.", 4 "metadata": {"title": "Apify"} 5}
This dataset is then processed by the Pinecone integration.
In the integration settings you need to specify which fields you want to save to Pinecone, e.g., ["text"] and which of them should be used as metadata, e.g., {"title": "metadata.title"}.
Without any other configuration, the data is saved to Pinecone as is.
1{ 2 "datasetFields": ["text"], 3 "metadataDatasetFields": {"title": "metadata.title"} 4}
Create chunks from Website Content Crawler data and save them to the database
Assume that the text data from the Website Content Crawler is too long to compute embeddings.
Therefore, we need to divide the data into smaller pieces called chunks.
We can leverage LangChain's RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter to split the text into chunks and save them into a database.
The parameters chunkSize and chunkOverlap are important.
The settings depend on your use case where a proper chunking helps optimize retrieval and ensures accurate responses.
1{ 2 "datasetFields": ["text"], 3 "metadataDatasetFields": {"title": "metadata.title"}, 4 "performChunking": true, 5 "chunkSize": 1000, 6 "chunkOverlap": 0 7}
Configure update strategy
To control how the integration updates data in the database, use the dataUpdatesStrategy parameter. This parameter allows you to choose between different update strategies based on your use case, such as adding new data, upserting records, or incrementally updating records based on changes (deltas). Below are the available strategies and explanations for when to use each:
-
Add data (
add):- Appends new data to the database without checking for duplicates or updating existing records.
- Suitable for cases where deduplication or updates are unnecessary, and the data simply needs to be added.
- For example, you might use this strategy to continually append data from independent crawls without regard for overlaps.
-
Upsert data (
upsert):- Delete existing records in the database if they match a key or identifier and inserts new records.
- Ideal when you want to maintain accurate and up-to-date data while avoiding duplication.
- For instance, this is useful in cases where unique items (such as user profiles or documents) need to be managed, ensuring the database reflects the latest changes.
- Check the
dataUpdatesPrimaryDatasetFieldsparameter to specify which fields are used to uniquely identify each dataset item.
-
Delta updates (
deltaUpdates):- Incrementally updates records by identifying differences (deltas) between the new dataset and the existing database records.
- Ensures only new or modified records are processed, leaving unchanged records untouched. This minimizes unnecessary database operations and improves efficiency.
- This is the most efficient strategy when integrating data that evolves over time, such as website content or recurring crawls.
- Check the
dataUpdatesPrimaryDatasetFieldsparameter to specify which fields are used to uniquely identify each dataset item.
Incrementally update database from the Website Content Crawler
To incrementally update data from the Website Content Crawler to database, configure the integration to update only the changed or new data.
This is controlled by the dataUpdatesStrategy setting.
This way, the integration minimizes unnecessary updates and ensures that only new or modified data is processed.
A checksum is computed for each dataset item (together with all metadata) and stored in the database alongside the vectors.
When the data is re-crawled, the checksum is recomputed and compared with the stored checksum.
If the checksum is different, the old data (including vectors) is deleted and new data is saved.
Otherwise, only the last_seen_at metadata field is updated to indicate when the data was last seen.
Provide unique identifier for each dataset item
To incrementally update the data, you need to be able to uniquely identify each dataset item.
The variable dataUpdatesPrimaryDatasetFields specifies which fields are used to uniquely identify each dataset item and helps track content changes across different crawls.
For instance, when working with the Website Content Crawler, you can use the URL as a unique identifier.
1{ 2 "dataUpdatesStrategy": "deltaUpdates", 3 "dataUpdatePrimaryDatasetFields": ["url"] 4}
Additionally, you can use the usePineconeIdPrefix parameter to optimize delta updates by creating a Pinecone-specific ID prefix in the database instead of storing metadata.
The prefix is auto generated using the format: item_id#chunk_id, which results in more efficient updates.
1{ 2 "dataUpdatesStrategy": "deltaUpdates", 3 "dataUpdatePrimaryDatasetFields": ["url"], 4 "usePineconeIdPrefix": true 5}
To fully maximize the potential of incremental data updates, it is recommended to start with an empty database. While it is possible to use this feature with an existing database, records that were not originally saved using a prefix or metadata will not be updated.
Delete outdated (expired) data
The integration can delete data from the database that hasn't been crawled for a specified period, which is useful when data becomes outdated, such as when a page is removed from a website.
The deletion feature can be enabled or disabled using the deleteExpiredObjects setting.
For each crawl, the last_seen_at metadata field is created or updated.
This field records the most recent time the data object was crawled.
The expiredObjectDeletionPeriodDays setting is used to control number of days since the last crawl, after which the data object is considered expired.
If a database object has not been seen for more than the expiredObjectDeletionPeriodDays, it will be deleted automatically.
The specific value of expiredObjectDeletionPeriodDays depends on your use case.
- If a website is crawled daily,
expiredObjectDeletionPeriodDayscan be set to 7. - If you crawl weekly, it can be set to 30.
To disable this feature, set deleteExpiredObjects to false.
1{ 2 "deleteExpiredObjects": true, 3 "expiredObjectDeletionPeriodDays": 30 4}
💡 If you are using multiple Actors to update the same database, ensure that all Actors crawl the data at the same frequency. Otherwise, data crawled by one Actor might expire due to inconsistent crawling schedules.
💾 Outputs
This integration will save the selected fields from your Actor to Pinecone and store the chunked data in the Apify dataset.
🔢 Example configuration
Full Input Example for Website Content Crawler Actor with Pinecone integration
1{ 2 "pineconeApiKey": "YOUR-PINECONE-API-KEY", 3 "pineconeIndexName": "apify", 4 "embeddingsApiKey": "YOUR-OPENAI-API-KEY", 5 "embeddingsConfig": { 6 "model": "text-embedding-3-small" 7 }, 8 "embeddingsProvider": "OpenAI", 9 "datasetFields": [ 10 "text" 11 ], 12 "dataUpdatesStrategy": "deltaUpdates", 13 "dataUpdatePrimaryDatasetFields": ["url"], 14 "expiredObjectDeletionPeriodDays": 7, 15 "performChunking": true, 16 "chunkSize": 2000, 17 "chunkOverlap": 200 18}
Pinecone
1{ 2 "pineconeApiKey": "YOUR-PINECONE-API-KEY", 3 "pineconeIndexName": "apify" 4}
OpenAI embeddings
1{ 2 "embeddingsApiKey": "YOUR-OPENAI-API-KEY", 3 "embeddingsProvider": "OpenAI", 4 "embeddingsConfig": {"model": "text-embedding-3-large"} 5}
Cohere embeddings
1{ 2 "embeddingsApiKey": "YOUR-COHERE-API-KEY", 3 "embeddingsProvider": "Cohere", 4 "embeddingsConfig": {"model": "embed-multilingual-v3.0"} 5}
Pricing
Pricing model
Pay per usageThis Actor is paid per platform usage. The Actor is free to use, and you only pay for the Apify platform usage.



